
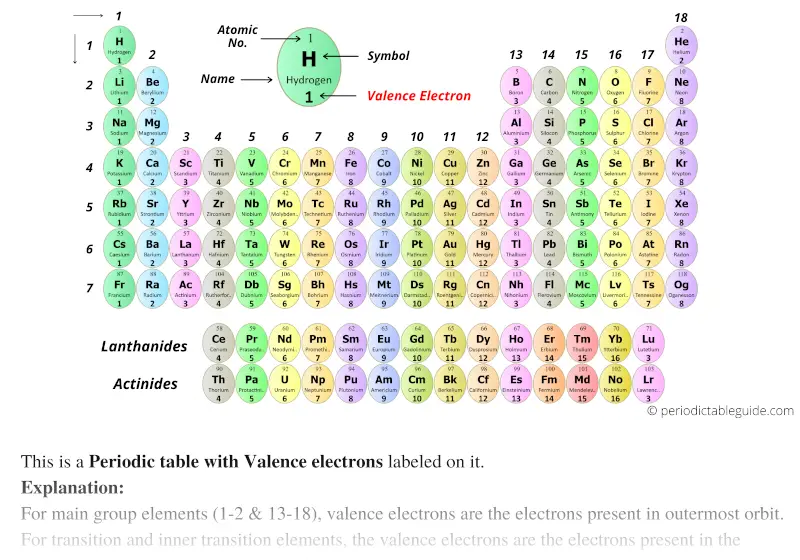
Take note of the transition metal’s position on the periodic table and its designation in the group. The majority of transitional metals have two valence electrons by strict definition, but they may have a wider range of apparent valence electrons than this. As a result, subshell electrons may behave similarly to valence electrons.
Periodic table valence electrons full#
In order to achieve a full subshell, an atom may preferentially accept or lose electrons from an incomplete subshell if doing so will result in a full subshell. Transitional metals, on the other hand, may contain subshells that are not completely filled.
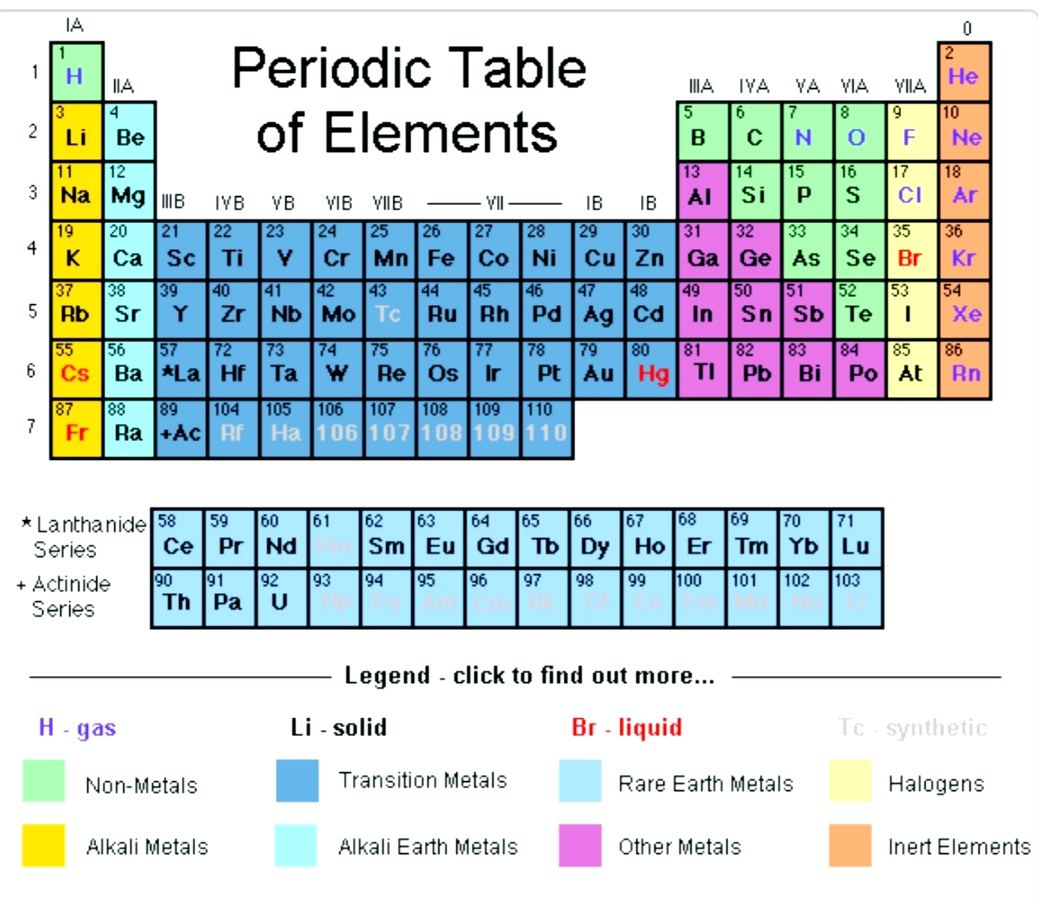
Valence electrons are typically the electrons that remain after all of an atom’s inner subshells have been filled with protons. Finding Valence Electrons for Transition Metals
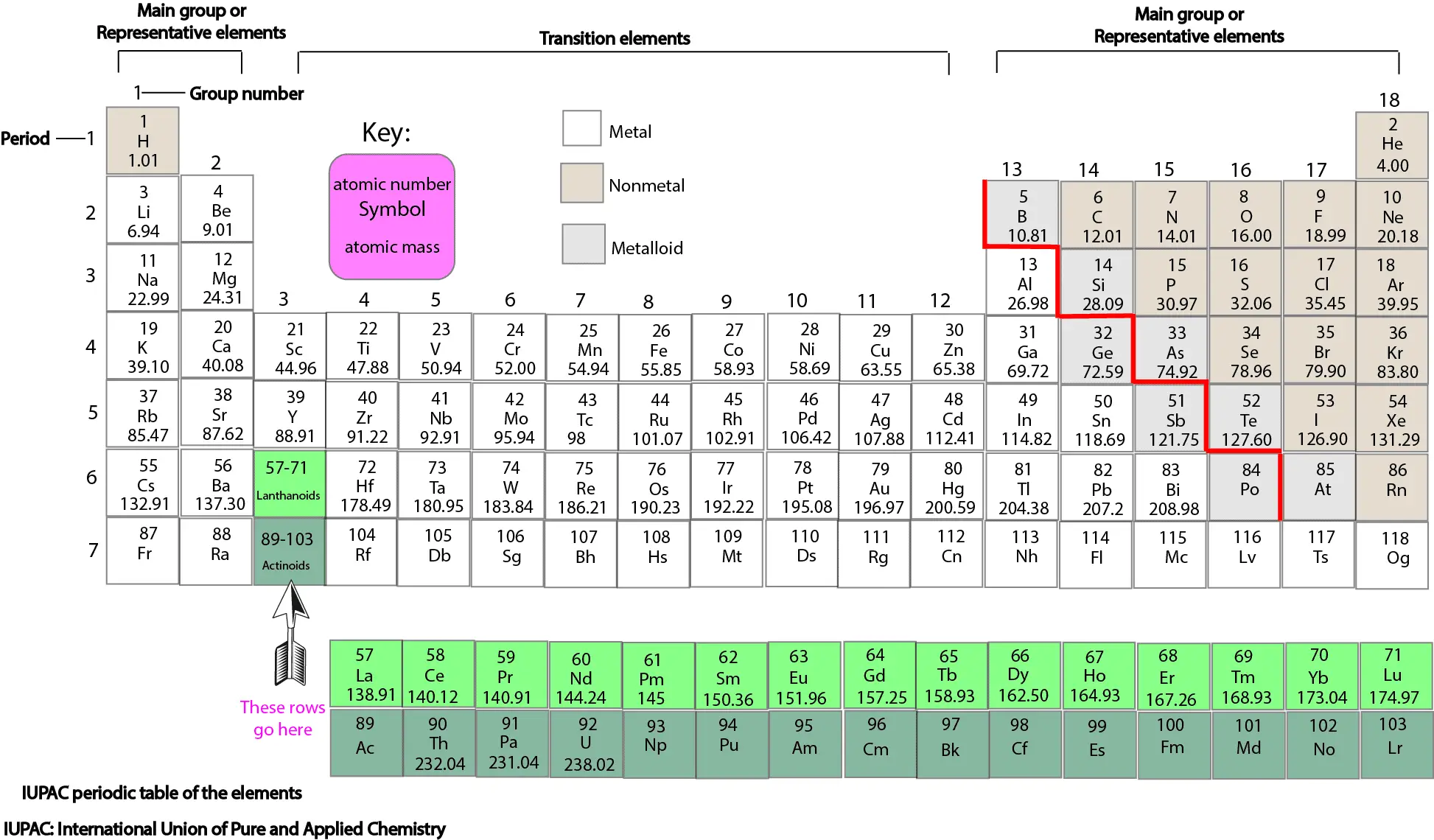
Except for helium, which has only two valence electrons, all of the elements in group 18 have eight valence electrons.ĭue to the fact that oxygen is found in group 16 of the periodic table, it contains six valence electrons. This is how you should behave in accordance with the rule: Each group contains one valence electron elements in group 2 contain two valence electrons elements in group 13 contain three valence electrons elements in group 14 contain four valence electrons and so on until the last group contains eight valence electrons. These are transitional metals, which are subjected to unique environmental conditions. Each new period starts with one valence electron, which is the first electron of the previous period. As a rule, the following is followed: If an element is not a transition metal, the number of valence electrons increases as you count groups from left to right along a period of time for that element. To make your element, follow the rules of the periodic table. Period 2, Group 16, contains the element oxygen. Periods are defined by the number of electron shells possessed by the atoms of the elements in a given row of the periodic table. Periods are the horizontal rows of the periodic table, which run from 1 to 7 in number. In the periodic table, elements with chemical properties that are similar are grouped together in the same group. Groups are the vertical columns of the periodic table that are counted from left to right, from 1 to 18. Symbolised by the letter “O,” oxygen has an atomic number of eight and is represented by the letter “O.”ĭetermine the element’s group number and period number by referring to the periodic table. Each square on the periodic table has the letter symbol for an element printed directly below the atomic number of the element in the square in question.Ĭonsider the element oxygen, which can be found on the table. Locate the element you’re looking for on the periodic table. Finding Valence Electrons for All Elements Except Transition Metals However, although the orbitals involved can be found in an inner electron shell and do not all correspond to a certain electron shell or principal quantum number n in the same element as one another, they are all located at relatively close distances to the nucleus in the same element. The orbitals of the incomplete (n-1)d subshell are included for transition metals, and the orbitals of the incomplete (n-2)f and (n-1)d subshells are included for lanthanides and actinides. The valence shell of main-group elements is made up of the ns and np orbitals, which are located in the outermost electron shell. As a result, valence electrons have a direct impact on the behaviour of elements during a chemical reaction. Atoms are more likely to accept or lose electrons if doing so will result in the completion of their outer shell. The valence electrons of an atom travel in the subshell that is the furthest away from the nucleus of the atom, according to its definition. Each electron shell is made up of one or more subshells, which are themselves composed of electrons. Electrons orbit around the atomic nuclei at specific energy levels, known as principal energy levels or electron shells, which are defined by the atom’s structure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
